«`html
La relación entre el cuadrado de la hipotenusa y los cuadrados de los catetos es un concepto fundamental en geometría que se aplica en el teorema de Pitágoras. Comprender esta relación es esencial para resolver problemas relacionados con triángulos rectángulos y aplicar este conocimiento en diversas áreas, incluyendo la ingeniería, la arquitectura y las ciencias físicas.
«`
«`html
El teorema de Pitágoras y su importancia
«`
«`html
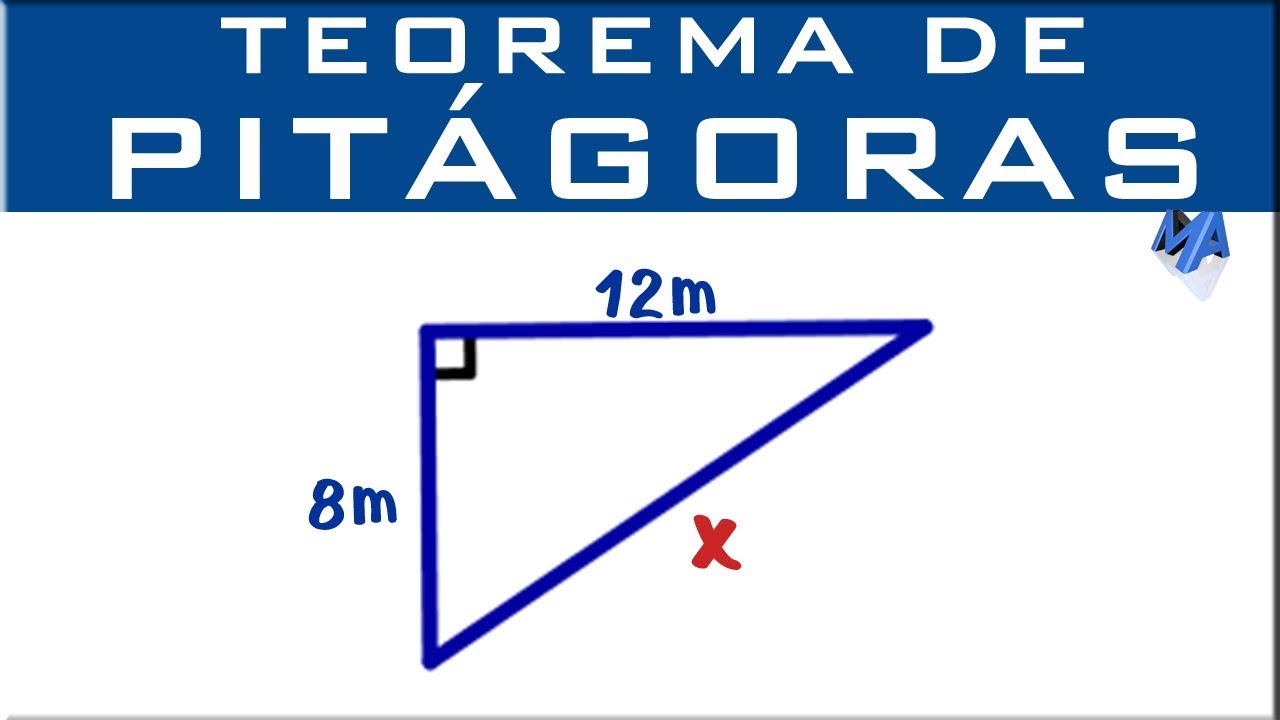
El teorema de Pitágoras es una de las premisas fundamentales en geometría y establece una relación matemática crucial entre los lados de un triángulo rectángulo. Este teorema afirma que en un triángulo rectángulo, el cuadrado de la longitud de la hipotenusa (el lado opuesto al ángulo recto) es igual a la suma de los cuadrados de las longitudes de los catetos (los dos lados que forman el ángulo recto). Matemáticamente se expresa como: a^2 + b^2 = c^2, donde «a» y «b» son las longitudes de los catetos y «c» es la longitud de la hipotenusa. Esta relación es esencial para resolver problemas relacionados con triángulos rectángulos y tiene amplias aplicaciones en diversas disciplinas.
«`
«`html
El concepto de triángulo rectángulo
«`
«`html
Un triángulo rectángulo es un tipo particular de triángulo que contiene un ángulo recto, es decir, un ángulo de 90 grados. Esta característica distingue al triángulo rectángulo de otros tipos de triángulos, y permite aplicar el teorema de Pitágoras y la relación entre el cuadrado de la hipotenusa y los cuadrados de los catetos. La hipotenusa es el lado opuesto al ángulo recto, mientras que los catetos son los dos lados que forman el ángulo recto. Esta disposición proporciona la base para establecer la relación matemática descrita por el teorema de Pitágoras.
«`
«`html
Proof of the Theorem
«`
«`html
The general proof of the theorem involves a combination of algebraic manipulation and geometric reasoning. One popular geometric proof involves the use of squares to demonstrate the relationship between the areas of the squares constructed on each side of the triangle. The manipulation of these squares visually illustrates the theorem and provides a clear justification for the mathematical relationship it represents. This proof has been a subject of interest and study for mathematicians and students throughout history.
«`
«`html
Applications in Real Life
«`
«`html
The relationship between the square of the hypotenuse and the squares of the legs has numerous applications in real life. From calculating distances in navigation and surveying to designing structures in architecture and engineering, the theorem of Pythagoras plays a pivotal role in various fields. Its applications extend into areas such as physics, where it is used to analyze vectors and forces, and even in computer science for algorithms and data analysis. Understanding and applying this relationship is essential for solving practical problems and advancing knowledge in diverse disciplines.
«`
«`html
Generalization to n-Dimensional Spaces
«`
«`html
While the theorem of Pythagoras is widely known for its application in two-dimensional geometry, its principles can be extended to n-dimensional spaces. The concept of the Pythagorean theorem transcends traditional Euclidean geometry and has implications in fields such as linear algebra and abstract mathematics. Generalizing the theorem to higher dimensions introduces new perspectives and insights into spatial relationships and is a key component in advanced mathematical studies.
«`
«`html
Challenges and Variations
«`
«`html
Exploring variations and extensions of the Pythagorean theorem presents interesting challenges for mathematicians and students alike. Different geometries, non-Euclidean spaces, and alternative metrics offer new scenarios where the traditional theorem may be modified or generalized. These variations not only test the understanding of the original concept but also spur innovation and creativity in mathematical thinking. Addressing these challenges leads to a deeper grasp of geometric principles and expands the applications of the theorem in increasingly diverse contexts.
«`
«`html
Historical Significance
«`
«`html
The theorem of Pythagoras has a rich historical significance, dating back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks. Its discovery and proof are attributed to the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, although evidence suggests that the principle was known and used by earlier cultures. The theorem’s widespread adoption and its incorporation into various mathematical and scientific developments throughout history underscore its enduring importance and influence. Its impact extends beyond mathematics, permeating into philosophy and culture as a symbol of the power of reason and discovery.
«`
«`html
Concluding Thoughts
«`
«`html
The relationship between the square of the hypotenuse and the squares of the legs, encapsulated in the theorem of Pythagoras, is a fundamental concept with broad implications and applications. Its role in geometry, mathematics, and real-world scenarios is profound, shaping our understanding of spatial relationships and serving as a cornerstone for diverse fields. Exploring its historical roots, generalizations, and variations offers a continual source of fascination and intellectual challenge. As we acknowledge the timeless relevance of this relationship, we appreciate its enduring impact on the world of knowledge and discovery.
«`